| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 삼성SDS
- 데이터 분석
- 혼공학습단
- 직원 이직률
- Brightics
- Brightics Studio
- 삼성SDS Brigthics
- 노코드AI
- 개인 의료비 예측
- 팀 분석
- 캐글
- Brightics를 이용한 분석
- 삼성SDS Brightics
- 직원 이직여부
- 삼성 SDS Brigthics
- Brigthics
- 모델링
- 혼공머신러닝딥러닝
- 영상제작기
- Brigthics를 이용한 분석
- 혼공머신
- 포스코 청년
- 혼공
- 데이터분석
- 브라이틱스
- 추천시스템
- 포스코 아카데미
- 브라이틱스 서포터즈
- 삼성 SDS
- Brigthics Studio
- Today
- Total
데이터사이언스 기록기📚
[이것이 취업을 위한 코딩테스트이다 with 파이썬] Ch.13 DFS/BFS 문제 본문
[이것이 취업을 위한 코딩테스트이다 with 파이썬] Ch.13 DFS/BFS 문제
syunze 2023. 4. 3. 15:57📌한 장으로 보는 알고리즘


DFS 문제풀이
- 스택 이용
- 재귀구조 이용
BFS 문제풀이
- 큐 이용 (파이썬 deque 사용)
📌Q.15 특정 거리의 도시 찾기
✔️문제 유형
그래프 이론, 그래프 탐색, 너비 우선 탐색, 데이크스트라
✔️문제
18352번: 특정 거리의 도시 찾기
첫째 줄에 도시의 개수 N, 도로의 개수 M, 거리 정보 K, 출발 도시의 번호 X가 주어진다. (2 ≤ N ≤ 300,000, 1 ≤ M ≤ 1,000,000, 1 ≤ K ≤ 300,000, 1 ≤ X ≤ N) 둘째 줄부터 M개의 줄에 걸쳐서 두 개
www.acmicpc.net
✔️나의 문제풀이
- 시간 초과
from collections import deque
import sys
n,m,k,x = map(int,input().split())
graph = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
for i in range(m):
a,b = map(int,sys.stdin.readline().split())
graph[a].append(b)
def bfs(a,k):
ans = 0
queue = deque()
queue.append((a,ans))
ans_list = []
while queue:
pos, distance = queue.popleft()
if distance == k:
ans_list.append(pos)
ans += 1
for i in range(len(graph[pos])):
if graph[pos][i] not in [queue[j][0] for j in range(len(queue))]:
queue.append((graph[pos][i],ans))
return ans_list
if len(bfs(x,k)) > 0:
new_list = sorted(list(bfs(x,k)))
for num in new_list:
print(num)
else:
print(-1)
✔️다른 사람의 문제풀이
- (모든 간선의 비용이 1) 그래프 모든 간선 비용 동일 → BFS로 최단거리 찾기
- N은 최대 300,000개, M은 최대 1,000,000 → 시간복잡도 O(N+M) 동작 코드 작성
- X에서 시작 → 모든 도시의 최단 거리 → 최단 거리 하나씩 확인하며 K인 경우 도시 번호 출력
from collections import deque
n,m,k,x = map(int,input().split())
graph = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
for _ in range(m):
a,b = map(int,input().split())
graph[a].append(b)
distance = [-1] * (n+1)
distance[x] = 0 # 출발 도시까지의 거리는 0으로 설정
# BFS
q = deque([x])
while q:
now = q.popleft()
for next_node in graph[now]:
if distance[next_node] == -1: # -1일 때만 바꿔서 '최소'거리 보장 가능
distance[next_node] = distance[now] + 1
q.append(next_node)
check = False
for i in range(1, n+1):
if distance[i] == k:
print(i)
check = True # 값이 존재한다는 의미로, 뒤에 if문 실행하지 않기 위한 조건
if check == False:
print(-1)
✔️리뷰
- BFS는 인덱스에 숫자를 더하는 형태로 정답을 도출하는 경우가 많음
(Part.2 미로탈출 참고) - 주어진 값을 '어떻게' 활용할 것인지 고민하기
📌Q.16 연구소
✔️문제 유형
구현, 그래프 이론, 브루트포스 알고리즘, 그래프 탐색, 너비 우선 탐색
✔️문제
14502번: 연구소
인체에 치명적인 바이러스를 연구하던 연구소에서 바이러스가 유출되었다. 다행히 바이러스는 아직 퍼지지 않았고, 바이러스의 확산을 막기 위해서 연구소에 벽을 세우려고 한다. 연구소는 크
www.acmicpc.net
✔️나의 문제풀이
X
✔️다른 사람의 문제풀이
아이디어 : 벽 3개 설치하는 모든 경우의 수 계산 → 안전 영역 계산 시 DFS,BFS(완전탐색) 적절히 이용
n,m = map(int,input().split())
data = []
temp = [[0] * m for _ in range(n)] # 벽을 설치한 뒤의 맵 리스트
for _ in range(n):
data.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
dx = [-1,0,1,0]
dy = [0,1,0,-1]
result = 0
# DFS를 이용해 각 바이러스가 사방으로 퍼지도록 하기
def virus(x,y):
for i in range(4):
nx = x + dx[i]
ny = y + dy[i]
# 상, 하, 좌, 우 중에서 바이러스가 퍼질 수 있는 경우
if nx >= 0 and nx < n and ny >= 0 and ny < m:
if temp[nx][ny] == 0:
# 해당 위치에 바이러스 배치하고, 다시 재귀적으로 수행
temp[nx][ny] = 2
virus(nx,ny)
# 현재 맵에서 안전 영역의 크기 계산하는 메서드
def get_score():
score = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if temp[i][j] == 0:
score += 1
return score
# DFS를 이용하여 울타리 설치, 매번 안전 영역의 크기 계산
def dfs(count):
global result
if count == 3:
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
temp[i][j] = data[i][j]
# 각 바이러스 위치에서 전파 진행
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if temp[i][j] == 2:
virus(i,j)
result = max(result, get_score())
return
# 빈 공간에 울타리 설치(완전탐색)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if data[i][j] == 0:
data[i][j] = 1
count += 1
dfs(count)
data[i][j] = 0
count -= 1
dfs(0)
print(result)
✔️리뷰
- 주어진 수가 적은 경우, for문을 이용한 완탐 or combination을 이용한 완탐으로 BFS,DFS 적용
📌Q.17 경쟁적 전염
✔️문제 유형
구현, 그래프 이론, 그래프 탐색, 너비 우선 탐색
✔️문제
18405번: 경쟁적 전염
첫째 줄에 자연수 N, K가 공백을 기준으로 구분되어 주어진다. (1 ≤ N ≤ 200, 1 ≤ K ≤ 1,000) 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에 걸쳐서 시험관의 정보가 주어진다. 각 행은 N개의 원소로 구성되며, 해당 위치
www.acmicpc.net
✔️나의 문제풀이
- 풀이 방법
- maps 입력 시, 바이러스 q에 담기 → 담은 q 정렬
- (bfs_ 함수) 상하좌우 인덱스 확인, maps에 값 대입, q에 대입, 다음 q값이랑 차이나는 경우 s -= 1
- q가 없어질때 or s가 0일때 까지 반복
from collections import deque
n,k = map(int,input().split())
maps = []
q = deque()
for i in range(n):
virus = list(map(int,input().split()))
for j in range(len(virus)):
if virus[j] != 0:
q.append((virus[j],i,j))
maps.append(virus)
# x-1, y-1로 찾기
s,x,y = map(int,input().split())
q = sorted(q, key = lambda x:x[0])
q = deque(q)
# 큐에 넣고, 확장하기 - 숫자가 끝날 부분은 구분하기
def bfs_(maps,q):
global s
num, x_p, y_p = q.popleft()
if x_p - 1 >= 0 and maps[x_p-1][y_p] == 0:
maps[x_p-1][y_p] = num # 하
q.append((num,x_p-1,y_p))
if x_p + 1 < n and maps[x_p+1][y_p] == 0:
maps[x_p+1][y_p] = num # 상
q.append((num,x_p+1,y_p))
if y_p - 1 >= 0 and maps[x_p][y_p-1] == 0:
maps[x_p][y_p-1] = num # 좌
q.append((num,x_p,y_p-1))
if y_p + 1 < len(maps) and maps[x_p][y_p+1] == 0:
maps[x_p][y_p+1] = num
q.append((num,x_p,y_p+1)) # 우
if len(q) > 0 and (num != q[0][0] and q[0][0] == 1):
s -= 1
return maps
while q:
if s == 0:
break
bfs_(maps,q)
print(maps[x-1][y-1])
✔️책의 문제풀이
아이디어 : 초기 큐에 원소 삽입할 때 낮은 번호부터 삽입 → BFS 이용, 방문하지 않은 위치 차례대로 방문
from collections import deque
n,k = map(int,input().split())
graph = [] # 전체 보드 정보를 담는 리스트
data = [] # 바이러스에 대한 정보를 담는 리스트
for i in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
for j in range(n):
if graph[i][j] != 0:
# (바이러스 종류, 시간, 위치 X, 위치 Y) 삽입
data.append((graph[i][j], 0, i, j))
data.sort()
q = deque(data)
target_s, target_x, target_y = map(int, input().split())
# 바이러스가 퍼져나갈 수 있는 4가지 위치
dx = [-1,0,1,0]
dy = [0,1,0,-1]
# BFS
while q:
virus, s, x, y = q.popleft()
if target_s == s:
break
for i in range(4):
nx = x + dx[i]
ny = y + dy[i]
if 0 <= nx and nx < n and 0 <= ny and ny < n:
if graph[nx][ny] == 0:
graph[nx][ny] = virus
q.append((virus, s+1, nx, ny))
print(graph[target_x-1][target_y-1])
✔️리뷰
- 변수명 겹치는거 없는지 잘 확인하기ㅠㅠ(num,n 같이 써서 오류나고 틀림 → 해결하니 성공)
- 걸리는 시간까지 q에 넣기
📌Q.18 괄호 변환
✔️문제유형
구현, DFS
✔️문제
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
✔️나의 문제풀이
- 문제 설명

- 나의 문제풀이 설명

# p 자체가 올바른 문자열일 때
def right(p):
total = 0
for i in range(len(p)):
if p[i] == '(':
total += 1
elif p[i] == ')':
total -= 1
if total >= 0:
continue
else:
return div(p)
return p
# u,v 판별부터 재귀
def div(p):
word_1, word_2 = 0,0
u = ''
for i in range(len(p)):
if p[i] == '(':
word_1 += 1
u += '('
elif p[i] == ')':
word_2 += 1
u += ')'
if word_1 == word_2:
break
v = p[word_1+word_2:]
return u,v
# u가 올바르지 않은 문자열일 때
def dfs(u,v):
if u == right(u):
return u + dfs(right(v)[0],right(v)[1])
else:
ans = '('
if v == right(v):
ans += v + ')'
else:
ans += dfs(right(v)[0],right(v)[1]) + ')'
u = u[1:-1]
u = list(u)
for i in range(len(u)):
if u[i] == '(':
u[i] = ')'
else:
u[i] = '('
return ans + ''.join(u)
def solution(p):
if p == '':
return ''
if p == right(p):
return p
else:
return dfs(right(p)[0],right(p)[1])
✔️다른 사람의 문제풀이
- 유사
# 균형잡힌 괄호 문자열의 인덱스 반환
def balanced_index(p):
count = 0 # 왼쪽 괄호의 개수
for i in range(len(p)):
if p[i] == '(':
count += 1
else:
count -= 1
if count == 0:
return i
# 올바른 괄호 문자열인지 판단
def check_proper(p):
count = 0
for i in p:
if i == '(':
count += 1
else:
if count == 0: # 쌍이 맞지 않는 경우 False
return False
count -= 1
return True
def solution(p):
answer = ''
if p == '':
return answer
index = balanced_index(p)
u = p[:index+1]
v = p[index+1:]
# 올바른 괄호 문자열이면, v에 대해 함수를 실행한 결과 붙여서 반환
if check_proper(u):
answer = u + solution(v)
else:
answer = '('
answer += solution(v)
answer += ')'
u = list(u[1:-1])
for i in range(len(u)):
if u[i] == '(':
u[i] = ')'
else:
u[i] = '('
answer += ''.join(u)
return answer📌Q.19 연산자 끼워 넣기
✔️문제 유형
브루트포스 알고리즘, 백트래팅
✔️문제
14888번: 연산자 끼워넣기
첫째 줄에 수의 개수 N(2 ≤ N ≤ 11)가 주어진다. 둘째 줄에는 A1, A2, ..., AN이 주어진다. (1 ≤ Ai ≤ 100) 셋째 줄에는 합이 N-1인 4개의 정수가 주어지는데, 차례대로 덧셈(+)의 개수, 뺄셈(-)의 개수,
www.acmicpc.net
✔️나의 문제풀이
- 성공
- 연산자 개수를 기호로 변경 -> 순열 만들어서 경우의 수 준비
- 주의!! max_,min_ 1e10으로 설정! (-10억,10억을 포함하고 있어 -10억,10억보다 큰 수로 설정해야 함)
- 차례대로 돌아가며 연산 계산
from itertools import permutations
n = int(input())
nums = list(map(int,input().split()))
opers = list(map(int,input().split())) # 차례대로 [덧셈, 뺄셈, 곱셈, 나눗셈]
oper_list = []
for i in range(len(opers)):
if i == 0:
for _ in range(opers[i]):
oper_list.append('+')
elif i == 1:
for _ in range(opers[i]):
oper_list.append('-')
elif i == 2:
for _ in range(opers[i]):
oper_list.append('*')
else:
for _ in range(opers[i]):
oper_list.append('//')
# nums-1개의 조합
per_list = list(permutations(oper_list, len(nums)-1))
per_list = set(per_list)
max_ = -1e10
min_ = 1e10
for per in per_list:
ans = nums[0]
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
if per[i] == '+':
ans = (ans + nums[i+1])
elif per[i] == '-':
ans = (ans - nums[i+1])
elif per[i] == '*':
ans = (ans * nums[i+1])
else:
if ans < 0 and nums[i+1] > 0:
ans = - (-ans//nums[i+1])
else:
ans = (ans//nums[i+1])
if ans > max_:
max_ = ans
if ans < min_:
min_ = ans
print(max_)
print(min_)
✔️다른 사람의 문제풀이
- add += 1, sub +=1을 하는 이유 : 전체 계산을 고려하기 위해 다시 원상태로 돌린 후, 다시 새로운 계산
# 백준 연산자 끼워 넣기
n = int(input())
data = list(map(int,input().split()))
add, sub, mul, div = map(int,input().split())
min_value = 1e9
max_value = -1e9
def dfs(i,now):
global min_value, max_value, add, sub, mul, div
# 모든 연산자를 다 사용한 경우, 최솟값과 최댓값 업데이트
if i == n:
min_value = min(min_value, now)
max_value = max(max_value, now)
else:
if add > 0:
add -= 1
dfs(i+1, now+data[i])
add += 1
if sub > 0:
sub -= 1
dfs(i+1, now-data[i])
sub += 1
if mul > 0:
mul -= 1
dfs(i+1, now*data[i])
mul += 1
if div > 0:
div -= 1
dfs(i+1, int(now/data[i]))
div += 1
dfs(1,data[0])
print(max_value)
print(min_value)
✔️리뷰
- 직접 식을 만드는 형식이 아닌, 숫자와 재귀로 계산 가능
- 백트래킹 : 가능한 모든 방법을 탐색, 가지치기를 통해 효율을 극대화(가능성이 없는 루트를 가지치기로 쳐내며 탐색)
→ DFS의 비효율적인 경로 차단
[알고리즘] 백트래킹(BackTracking)
백준 문제를 풀면서 알고리즘도 같이 정리해두면 좋을 것 같아서 정리해보겠다-! 💡 백트래킹 백트리킹이란 "가능한 모든 방법을 탐색한다"의 아이디어를 가진다. 즉, 백트래킹은 현재 상태에
velog.io
- 브루트포스 알고리즘 : 완전탐색 알고리즘(모든 경우의 수 고려)
알고리즘 기법[전체 탐색] - 브루트 포스(brute force)
암호학에서의 브루트 포스(brute force attack)가 아닌 알고리즘의 브루트 포스(brute force search)에 관한 것을 작성한다. 브루트 포스(brute force) brute: 무식한, force: 힘 무식한 힘으로 해석할 수 있다. 완
hcr3066.tistory.com
📌Q.20 감시 피하기
✔️문제 유형
브루트포스 알고리즘, 백트래킹
✔️문제
18428번: 감시 피하기
NxN 크기의 복도가 있다. 복도는 1x1 크기의 칸으로 나누어지며, 특정한 위치에는 선생님, 학생, 혹은 장애물이 위치할 수 있다. 현재 몇 명의 학생들은 수업시간에 몰래 복도로 빠져나왔는데, 복
www.acmicpc.net
✔️나의 문제풀이
- 틀림
n = int(input())
maps = []
s_point = []
t_point = []
o_point = []
for i in range(n):
maps.append(list(map(str,input().split())))
for j in range(n):
if maps[i][j] == 'S':
s_point.append((i,j))
elif maps[i][j] == 'T':
t_point.append((i,j))
for s_x, s_y in s_point:
for t_x, t_y in t_point:
if s_x == t_x:
max_ = max(s_y,t_y)
min_ = min(s_y,t_y)
list_ = []
for i in range(min_+1,max_):
if (s_x,i) not in s_point:
list_.append((s_x,i))
o_point.append(list_)
elif s_y == t_y:
max_ = max(s_x,t_x)
min_ = min(s_x,t_x)
list_ = []
for i in range(min_+1,max_):
if (i,s_y) not in s_point:
list_.append((i,s_y))
o_point.append(list_)
same = sum(o_point,[])
same_li = [k for k in same if same.count(k) > 1]
same_li = list(set(same_li))
# print(same_li)
if len(same_li) > 0:
for i in range(len(o_point)):
for j in range(len(same_li)):
if same_li[j] in o_point[i]:
o_point[i].remove(same_li[j])
for o_list in o_point:
if len(o_list) == 0:
o_point.remove(o_list)
if len(o_point) > 3:
print('NO')
else:
print('YES')
✔️책의 문제풀이
아이디어 : 모든 조합이 10,000이하의 수로 완점탐색을 실행해도 시간초과 안 남.
1) 모든 조합을 찾기 위해 DFS나 BFS로 모든 조합을 반환하는 함수 작성
2) 파이썬 조합 라이브러리
- 선생님 위치 기준, 상하좌우 학생이 있는지 확인
from itertools import combinations
n = int(input())
board = []
teachers = []
spaces = [] # 모든 빈 공간 위치정보
for i in range(n):
board.append(list(input().split()))
for j in range(n):
if board[i][j] == 'T':
teachers.append((i,j))
if board[i][j] == 'X':
spaces.append((i,j))
# 특정방향으로 감시를 진행
def watch(x,y, direction):
if direction == 0:
while y >= 0:
if board[x][y] == 'S':
return True
if board[x][y] == 'O':
return False
y -= 1
if direction == 1:
while y < n:
if board[x][y] == 'S':
return True
if board[x][y] == 'O':
return False
y += 1
if direction == 2:
while x >= 0:
if board[x][y] == 'S':
return True
if board[x][y] == 'O':
return False
x -= 1
if direction == 3:
while x < n:
if board[x][y] == 'S':
return True
if board[x][y] == 'O':
return False
x += 1
return False
# 장애물 설치 이후, 한 명이라도 학생이 감지되는지 검사
def process():
for x,y in teachers:
for i in range(4):
if watch(x,y,i):
return True
return False
find = False
for data in combinations(spaces,3):
# 장애물 설치해보기
for x,y in data:
board[x][y] = 'O'
# 학생이 한 명도 감지되지 않는 경우
if not process():
find = True
break
# 설치된 장애물을 다시 없애기
for x,y in data:
board[x][y] = 'X'
if find:
print('YES')
else:
print('NO')
✔️리뷰
- 생각해야할 부분이 많고 연산량이 적으면 조합도 생각해보기
- 파이썬 2차원 리스트 언패킹
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
📌Q.21 인구이동
✔️문제 유형
구현, 그래프 이론, 그래프 탐색, 너비 우선 탐색, 시뮬레이
✔️문제
16234번: 인구 이동
N×N크기의 땅이 있고, 땅은 1×1개의 칸으로 나누어져 있다. 각각의 땅에는 나라가 하나씩 존재하며, r행 c열에 있는 나라에는 A[r][c]명이 살고 있다. 인접한 나라 사이에는 국경선이 존재한다. 모
www.acmicpc.net
✔️나의 문제풀이
- 문제 풀지 못함
- Ch.5의 음료수 얼려먹기와 유사하다 생각
n,l,r = map(int,input().split())
graph = []
for _ in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
open = [[1 for _ in range(len(graph[0]))] for _ in range(len(graph))]
# 국경선 열림
def dfs_open(graph, l,r):
for x in range(len(graph)-1):
for y in range(len(graph[0])-1):
if l <= abs(graph[x][y] - graph[x][y+1]) <= r:
open[x][y], open[x][y+1] = 0, 0
if l <= abs(graph[x+1][y] - graph[x][y]) <= r:
open[x+1][y], open[x][y] = 0, 0
if l <= abs(graph[x+1][y] - graph[x+1][y+1]) <= r:
open[x+1][y], open[x+1][y+1] = 0, 0
return open
# 만약 open이 0이면(bfs 사용하여 0인 부분 묶어서 계산), 계산 수행
# open 초기화 후, dfs_open 반복 수행 -> dfs 반복 수행
def dfs(x,y):
print(dfs_open(graph, l,r))
✔️다른 사람의 문제풀이
from collections import deque
n,l,r = map(int,input().split())
graph = []
for _ in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
dx = [-1,0,1,0]
dy = [0,-1,0,1]
result = 0
# 특정 위치에서 출발하여 모든 연합을 체크한 뒤에 데이터 갱신
def process(x,y,index):
# (x,y)의 위치와 연결된 나라 정보를 담는 리스트
united = []
united.append((x,y))
# deque는 연결되는 연합 확인하기 위한 도구
q = deque()
q.append((x,y))
union[x][y] = index # 현재 연합의 번호 할당
summary = graph[x][y] # 현재 연합의 전체 인구 수
count = 1 # 현재 연합 국가 수
while q:
x,y = q.popleft()
for i in range(4):
nx = x + dx[i]
ny = y + dy[i]
if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < n and union[nx][ny] == -1:
if l <= abs(graph[nx][ny] - graph[x][y]) <= r:
q.append((nx,ny))
# 연합에 추가
union[nx][ny] = index
summary += graph[nx][ny]
count += 1
united.append((nx,ny))
for i, j in united:
graph[i][j] = summary // count
return count
total_count = 0
# 더 이상 인구 이동을 할 수 없을 때까지 반복
while True:
union = [[-1] * n for _ in range(n)]
index = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if union[i][j] == -1:
process(i,j,index)
index += 1
if index == n * n:
break
total_count += 1
print(total_count)
✔️리뷰
- 구현 작성 코드와 유사한 부분 있음
(nx,ny와 x,y 확인 → nx, ny를 새로 만들어서 조건에 맞는지 확인하기)
📌Q.22 블록 이동하기
✔️문제
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
✔️나의 문제풀이
- 좌표가 안바뀌어서 실패, DFS로 풀었음
def dfs_(first,second,board,answer):
while True:
f_x,f_y = first
s_x, s_y = second
if s_x == len(board) and s_y == len(board):
return answer
if board[f_x][f_y+1] == 0 and board[s_x][s_y+1] == 0:
first, second = (f_x,f_y+1),(s_x, s_y+1)
dfs_(first, second,board,answer)
if board[f_x+1][f_y] == 0 and board[s_x+1][s_y] == 0:
first, second = (f_x+1, f_y), (s_x+1, s_y)
dfs_(first, second,board,answer)
if board[f_x+1][f_y+1] == 0 and board[f_x][f_y] == 0 and board[f_x+1][f_y] == 0:
first, second = (f_x,f_y), (f_x+1,f_y)
dfs_(first, second,board,answer)
if board[s_x+1][s_y-1] == 0 and board[s_x+1][s_y] == 0 and board[s_x][s_y] == 0:
first, second = (s_x+1, s_y), (s_x, s_y)
dfs_(first, second,board,answer)
answer += 1
def solution(board):
answer = 0
return dfs_((1,1),(1,2),board,answer)
✔️다른 사람의 문제풀이
- 아이디어 : 간선의 비용이 모두 1로 동일,(1,1)을 (n,n)으로 옮기는 최단거리 계산 → BFS로 최적의 해 구함
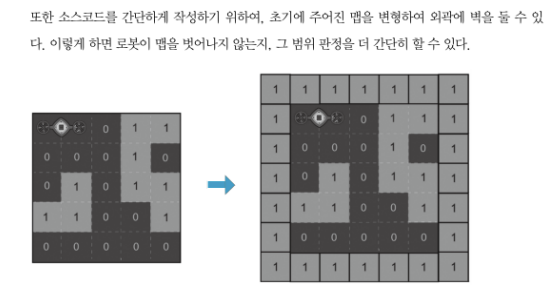
- 외곽에 벽을 두어 범위 판정
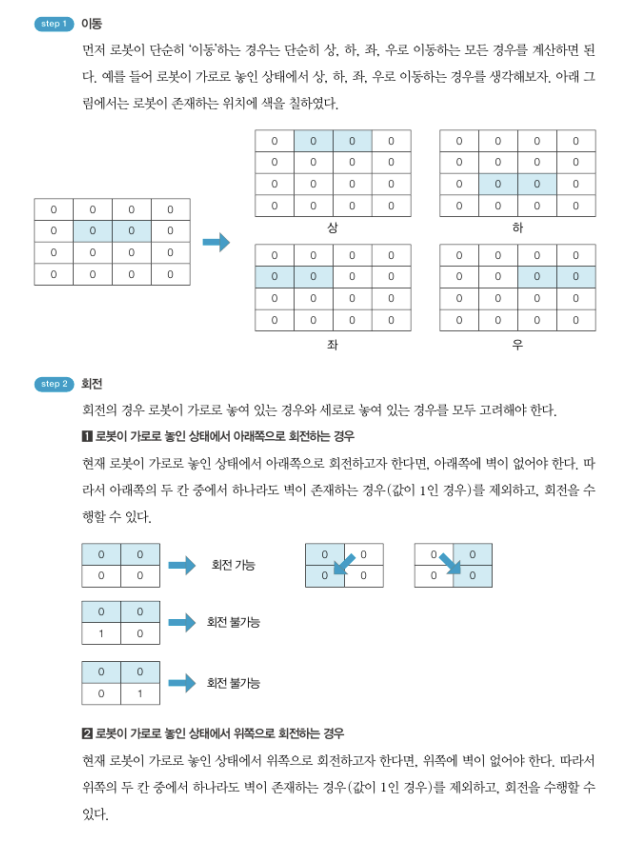
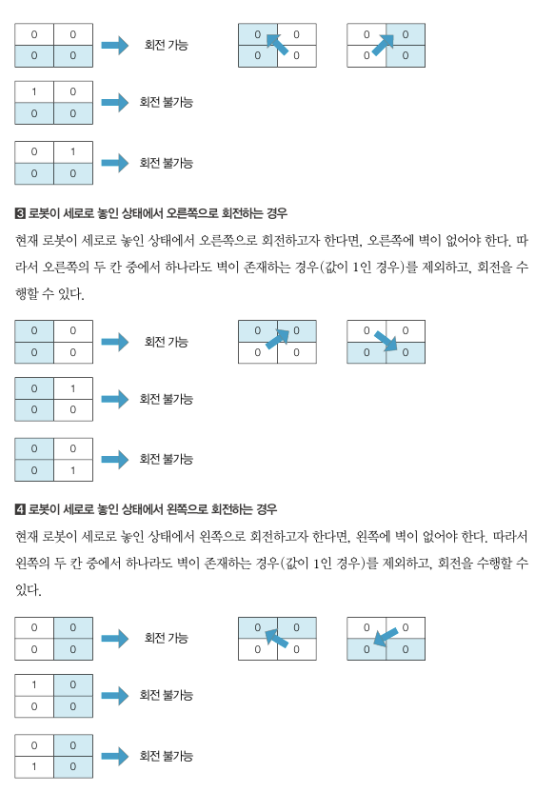
from collections import deque
def get_next_pos(pos, board):
next_pos = [] # 반환 결과(이동 가능한 위치들)
pos = list(pos) # 현재 위치 정보를 리스트로 변환(집합 -> 리스트)
pos1_x, pos1_y, pos2_x, pos2_y = pos[0][0], pos[0][1], pos[1][0], pos[1][1]
dx = [-1,1,0,0]
dy = [0,0,-1,1]
for i in range(4):
pos1_next_x, pos1_next_y, pos2_next_x, pos2_next_y = pos1_x+dx[i], pos1_y+dy[i],pos2_x+dx[i],pos2_y+dy[i]
# 이동하고자 하는 두 칸이 모두 비어있다면
if board[pos1_next_x][pos1_next_y] == 0 and board[pos2_next_x][pos2_next_y] == 0:
next_pos.append({(pos1_next_x, pos1_next_y), (pos2_next_x, pos2_next_y)})
# 현재 로봇이 가로로 놓여 있는 경우
if pos1_x == pos2_x:
for i in [-1,1]: # 위쪽으로 회전하거나, 아래쪽으로 회전
if board[pos1_x+i][pos1_y] == 0 and borad[pos2_x+i][pos2_y] == 0: #위,아래
next_pos.append({(pos1_x, pos1_y), (pos1_x+i, pos1_y)})
next_pos.append({(pos2_x, pos2_y), (pos2_x+i, pos2_y)})
# 현재 로봇이 세로로 놓여 있는 경우
elif pos1_y == pos2_y:
for i in [-1,1]:
if board[pos1_x][pos1_y+i] == 0 and borad[pos2_x][pos2_y+i] == 0:
next_pos.append({(pos1_x, pos1_y), (pos1_x, pos1_y+i)})
next_pos.append({(pos2_x, pos2_y), (pos2_x, pos2_y+i)})
return next_pos
def solution(board):
# 맵을 외곽에 벽을 두는 형태로 맵 변형
n = len(board)
new_board = [[1] * (n+2) for _ in range(n+2)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
new_board[i+1][j+1] = board[i][j]
# BFS 수행
q = deque()
visited = []
pos = {(1,1), (1,2)}
q.append((pos,0))
visited.append(pos)
while q:
pos, cost = q.popleft()
if (n,n) in pos:
return cost
# 현재 위치에서 이동할 수 있는 위치 확인
for next_pos in get_next_pos(pos, new_board):
# 아직 방문하지 않은 위치라면, 큐에 삽입하고 방문 처리
if next_pos not in visited:
q.append((next_pos, cost+1))
visited.append(next_pos)
return 0
✔️리뷰
- 모든 경우의 수 다 생각해보기
'Coding Test > 이것이 취업을 위한 코딩테스트이다 with 파이썬' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [이것이 취업을 위한 코딩테스트이다 with 파이썬] Ch.10 그래프 이론 (0) | 2023.04.11 |
|---|---|
| [이것이 취업을 위한 코딩테스트이다 with 파이썬] Ch.16 다이나믹 프로그래밍 문제 (0) | 2023.03.29 |
| [이것이 취업을 위한 코딩테스트이다 with 파이썬] Ch.12 구현 문제 (0) | 2023.03.22 |
| [이것이 취업을 위한 코딩테스트이다 with 파이썬] Ch.15 이진 탐색 문제 (0) | 2023.03.17 |
| [이것이 취업을 위한 코딩테스트다 with 파이썬] Ch.5 DFS/BFS (0) | 2023.03.07 |




